Top News
Why depression, anxiety are diagnosed more in women than men

Women are more frequently diagnosed with depression and anxiety and the taking of prescribed psychotropic drugs is also significantly higher among them, suggests a new study.
Gender is a significant determining factor in mental health and in how it is managed by the healthcare services, according to recent studies conducted on the basis of health questionnaires completed in the Basque Autonomous Community (2018) and in Spain (2017), and on the Spanish sample corresponding to the European Health Survey (2014).
The UPV/EHU’s research group OPIK, Social Determinants of Health and Demographic Change, is a multidisciplinary group comprising research personnel in the field of social and health sciences; it explores the social factors influencing health and disease in the population, social inequalities in health and the policies that have the potential to modify these social determinants in the interests of improving the health of the population.
What stands out in the analysis of these three databases is the higher prevalence of poor mental health among women of all ages and across all social groups; in addition, there is a multiplier effect due to the accumulation of experiences of inequality. This reality also appears to be unequal in terms of the age and socioeconomic level of the patients.
Amaia Bacigalupe, one of the authors of the study, asserts that “women are more frequently diagnosed with depression and anxiety and the taking of prescribed psychotropic drugs is also significantly higher, even if there is no difference with men with respect to mental health equality, diagnoses and frequency of visits to healthcare centres.
“All this could point to the existence of a medicalisation process of mental health in women, but interpreting its origin is complex since the processes involving the high prevalence of diagnosis and overprescription undoubtedly play a role, but maybe also due to infra-diagnosis and lower prescription rates in men”.
Bacigalupe adds that these aspects should be tackled in greater depth in future studies.
Reducing gender inequalities
The research group highlights the fact that reducing gender inequalities in mental health will need to be the result of policy intervention on various levels. “There is a clear relationship between the degree of gender inequality in society and gender inequalities in mental health,” says Amaia Bacigalupe.
“So all those policies designed to combat the discrimination endured by women on the labour market, in the responsibility for domestic and care work, in the use of time and, generally, relating to those that empower women on the basis of their greater political representation and making them more socially visible, will exert a positive effect on the reduction in mental inequalities between men and women”.
Another aspect highlighted in the study is the need to make commitments starting from an institutional level and geared towards curbing the medicalisation of everyday malaise from a clear gender perspective. “In the field of mental health in which the medicalisation of malaise is especially common, far from addressing the cause of the problem, some problems of a social origin end up receiving psychiatric or psychological treatment,” said the researcher in the Department of Sociology 2 at the UPV/EHU.
According to the study, it would also be necessary to encourage spaces for reflection in the clinical setting designed to help to collectively deconstruct certain aspects that have become natural in gender binarism and which have underpinned the definitions of psychopathology and its current treatment. Bacigalupe also says that “the actual incorporation into clinical practice of the biopsychosocial model, as well as the implementing of strategies to promote health and emotional well-being from a community health approach based on assets, could prevent the over-pathologization and over-medicalization of everyday malaise once a global view of how the social context influences health is acquired”.
Entertainment
Casino Days Reveal Internal Data on Most Popular Smartphones
International online casino Casino Days has published a report sharing their internal data on what types and brands of devices are used to play on the platform by users from the South Asian region.
Such aggregate data analyses allow the operator to optimise their website for the brands and models of devices people are actually using.
The insights gained through the research also help Casino Days tailor their services based on the better understanding of their clients and their needs.
Desktops and Tablets Lose the Battle vs Mobile
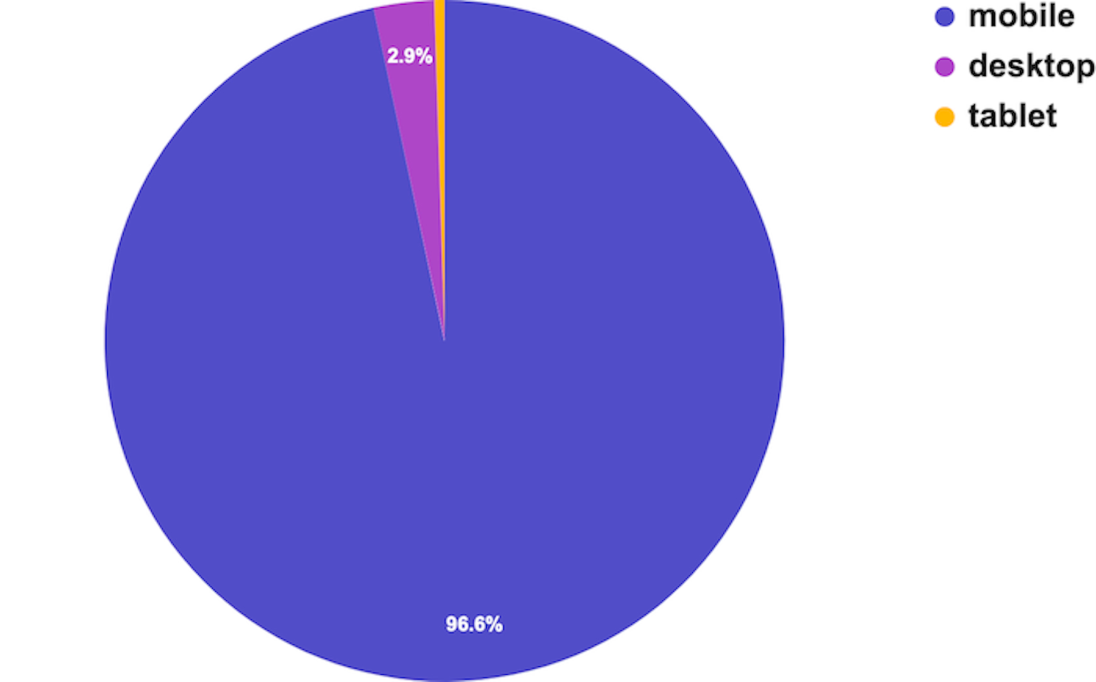
The primary data samples analysed by Casino Days reveal that mobile connections dominate the market in South Asia and are responsible for a whopping 96.6% of gaming sessions, while computers and tablets have negligible shares of 2.9% and 0.5% respectively.
The authors of the study point out that historically, playing online casino was exclusively done on computers, and attribute thе major shift to mobile that has unfolded over time to the wide spread of cheaper smartphones and mobile data plans in South Asia.
“Some of the reasons behind this massive difference in device type are affordability, technical advantages, as well as cheaper and more obtainable internet plans for mobiles than those for computers,” the researchers comment.
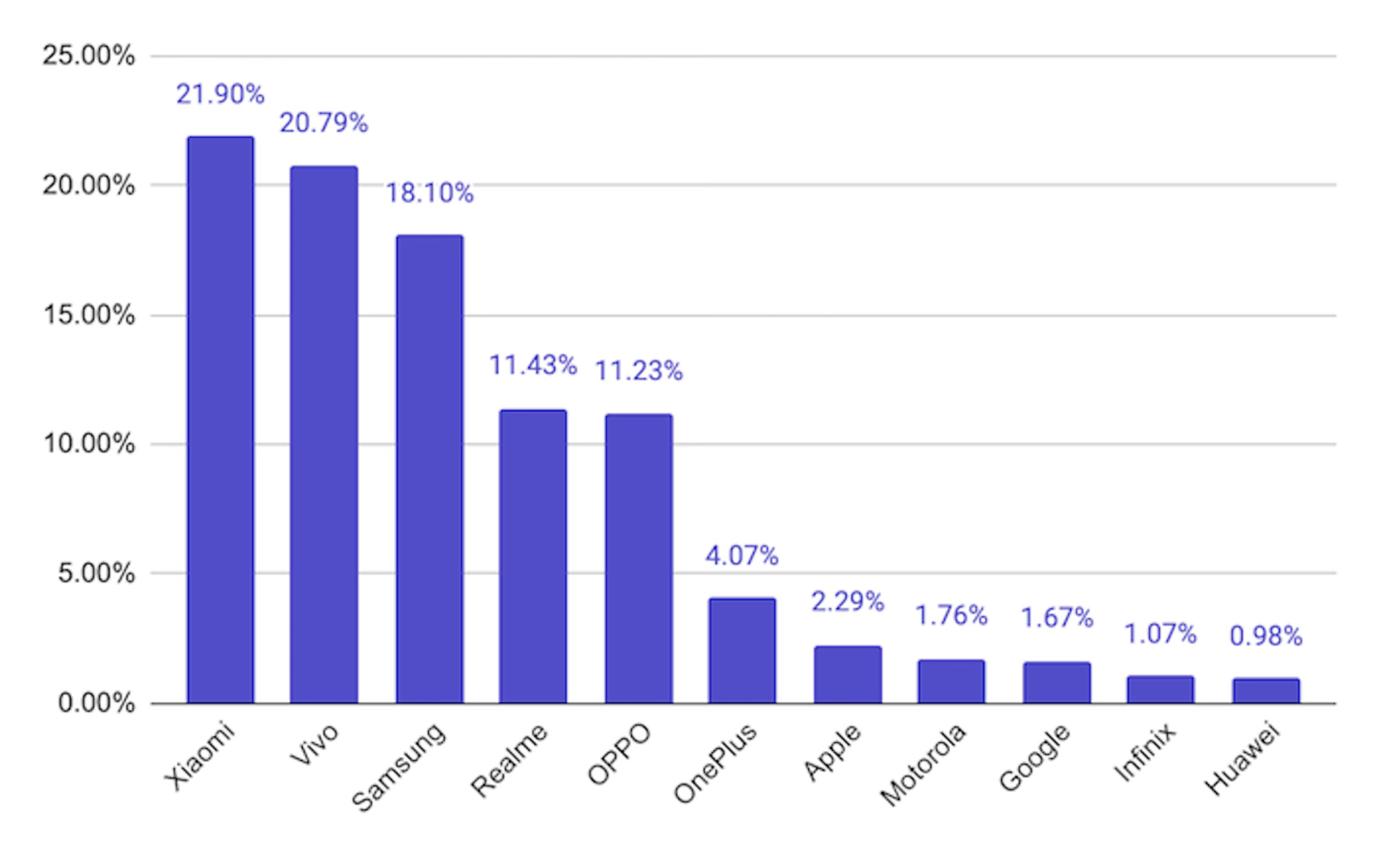
Xiaomi and Vivo Outperform Samsung, Apple Way Down in Rankings
Chinese brands Xiaomi and Vivo were used by 21.9% and 20.79% of Casino Days players from South Asia respectively, and together with the positioned in third place with a 18.1% share South Korean brand Samsung dominate the market among real money gamers in the region.
Cupertino, California-based Apple is way down in seventh with a user share of just 2.29%, overshadowed by Chinese brands Realme (11.43%), OPPO (11.23%), and OnePlus (4.07%).
Huawei is at the very bottom of the chart with a tiny share just below the single percent mark, trailing behind mobile devices by Motorola, Google, and Infinix.
The data on actual phone usage provided by Casino Days, even though limited to the gaming parts of the population of South Asia, paints a different picture from global statistics on smartphone shipments by vendors.
Apple and Samsung have been sharing the worldwide lead for over a decade, while current regional leader Xiaomi secured their third position globally just a couple of years ago.
Striking Android Dominance among South Asian Real Money Gaming Communities
The shifted market share patterns of the world’s top smartphone brands in South Asia observed by the Casino Days research paper reveal a striking dominance of Android devices at the expense of iOS-powered phones.
On the global level, Android enjoys a comfortable lead with a sizable 68.79% share which grows to nearly 79% when we look at the whole continent of Asia. The data on South Asian real money gaming communities suggests that Android’s dominance grows even higher and is north of the 90% mark.
Among the major factors behind these figures, the authors of the study point to the relative affordability of and greater availability of Android devices in the region, especially when manufactured locally in countries like India and Vietnam.
“And, with influencers and tech reviews putting emphasis on Android devices, the choice of mobile phone brand and OS becomes easy; Android has a much wider range of products and caters to the Asian online casino market in ways that Apple can’t due to technical limitations,” the researchers add.
The far better integration achieved by Google Pay compared to its counterpart Apple Pay has also played a crucial role in shaping the existing smartphone market trends.
Content provided by Adverloom